More Information
Submitted: December 19, 2025 | Approved: December 29, 2025 | Published: December 30, 2025
How to cite this article: Bhandari PN, Bhandari NM. Reimagining Reality: Consciousness, External Energy, and the Space-Time Quantum as the Foundation of Physics. Int J Phys Res Appl. 2025; 8(12): 303-315. Available from:
https://dx.doi.org/10.29328/journal.ijpra.1001140
DOI: 10.29328/journal.ijpra.1001140
Copyright license: © 2025 Bhandari PN, et al. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is propeRLy cited.
Keywords: Space-Time quantum*; Time (Intrinsic Frequency Reciprocal)*; External energy source; Asymmetry; Consciousness; Wave-particle duality; Entropy and arrow of time; Unified theoretical framework
Reimagining Reality: Consciousness, External Energy, and the Space-Time Quantum as the Foundation of Physics
Pushpak N Bhandari1 and Nandan M Bhandari2*
1J-253, MIDC, Bhosari, Pune 411026, India
2MSc, University of Saskatchewan, Canada
*Address for Correspondence: Nandan M Bhandari, J-253, MIDC, Bhosari, Pune 411026, India, Email: [email protected]
This paper introduces a theoretical framework that bridges the conceptual divide between quantum mechanics and relativity by proposing a fundamental building block of the universe: the “Space-Time* quantum.” The theory posits that every object possesses an inherent property, Time* — defined as the reciprocal of its intrinsic frequency. The Space-Time* quantum is a composite entity, consisting of a timeless space energy and a kinetic Time* energy. This framework provides a new perspective on wave-particle duality, the double-slit experiment, and quantum entanglement. It re-examines the principles of Special Relativity, offering a conceptual and visual explanation of phenomena such as time dilation and length contraction as a consequence of changes in the Space-Time quanta. The theory also provides an alternative view on the origin of the universe and the nature of gravity, suggesting that gravitational effects arise from an energy deficiency rather than a curvature of spacetime. This paper establishes a conceptual foundation for further mathematical development to test and validate these new insights.
The unification challenge
The quest to reconcile quantum mechanics and general relativity often leads to highly complex mathematical constructs. This paper explores a more intuitive, geometric alternative. We propose that the universe is driven by external energy from Space and Time dimensions, and that what we perceive as "forces" are actually manifestations of energy deficiencies (shadows) cast by matter within this external flow.
This paper presents a new theoretical framework that provides a unified and intuitive foundation for these disparate theories. We propose a new conceptual entity, the “Space-Time* quantum,” as the fundamental building block of the universe. This theory posits that all matter and energy are composed of these quanta, each possessing an inherent property we call “Time*.” This framework offers a unified perspective on phenomena that have long defied a single explanation, including wave-particle duality, gravity, and the fundamental nature of time itself.
However, relativity proved inadequate for explaining phenomena at the micro scale, specifically failing to describe the behaviour of nature at subatomic levels within the quantum world. The quantum realm is often conceptualised as being divided into an “observed” and an “unobserved” world. A satisfactory explanation for the distinctions between these two states has remained elusive, leading to various philosophical and scientific statements, such as:
- “God does not play dice with the universe.” — Einstein
- “It is a ghost world at the subatomic scale.”
- “Shut up and do the calculation.” — Richard Feynman
- “It seems some new ideas are needed to explain the quantum world.” — Paul Dirac
As humans, we constantly strive to discover new ideas to deepen our understanding of the Universe and its fundamental principles. While Quantum Physics has been remarkably successful in accurately predicting outcomes, it is inherently statistical. It struggles to provide a causal understanding of phenomena such as wave-particle duality, the measurement problem, wave function collapse, entanglement, and superpositions. To advance scientific knowledge, it is crucial to re-evaluate fundamental assumptions and establish a clearer foundation for the Universe.
Special Relativity provided elegant explanations for several phenomena:
- Time dilation is influenced by speed and gravity.
- Space contraction at higher velocities.
- The increase in an object’s mass with speed.
- Gravity as the curvature of imaginary space-time.
Despite these explanations, the underlying mechanisms remain largely unaddressed. Special Relativity is founded on two postulates:
- The laws of physics are consistent in all inertial frames of reference.
- The speed of light in a vacuum is constant for all observers, irrespective of their relative motion.
Further conceptualisation and visualisation of these postulates are still needed. While Einstein’s integration of time and space was a monumental step in understanding the Universe, a more profound integration of “time*” with space is required to comprehend behaviour at the quantum level. Building upon the efforts of luminaries such as Galileo, Newton, Bohr, Pauli, Einstein, Heisenberg, Paul Dirac, Schrödinger, Planck, De Broglie, Stephen Hawking, Leonard Susskind, Michael Kaku and many more, this paper aims to contribute a further step in this ongoing quest, though it may not be the definitive one.
Thermodynamics
The increase of entropy and the arrow of time have been attributed to the expansion of space. However, the rationale behind the Big Bang theory is not entirely satisfactory, suggesting the need for a more comprehensive explanation. While the Big Bang theory is supported by observations of cosmic isotropy and the cosmic microwave background, an alternative theory is necessary if it impedes further scientific progress, provided it can also account for these supporting observations.
The conceptual framework: The space-time quantum*
The core of this theory rests on a fundamental distinction between conventional time and a new intrinsic property called Time*.
- Time (T): Conventional time, as measured by a clock, is a relative dimension.
- Time (T)*: An intrinsic, absolute property of every Space-Time* quantum, defined as the reciprocal of its intrinsic frequency (ν). Thus, T∗ = 1/ν.
A Space-Time* quantum is defined as a composite entity resulting from the interaction of a timeless space component and a kinetic Time* component. This quantum is a localised wave packet — a wave confined by a Gaussian envelope — which is created by an external, continuous energy source. This external energy is the true essence of reality.
The unobserved state of a Space-Time* quantum is a wave, described by a complex wave function. The act of observation collapses this wave function, localising the quantum to a specific point, which we perceive as a particle. This elegant model provides a direct physical interpretation of wave-particle duality.
This “ocean” of space-time* quanta, residing within the overall quantum space, establishes the fundamental basis of the Universe. This concept will be explained in greater detail later in the article. The 3-dimensional Universe, which we inhabit, is formed by external asymmetry introduced into an initially symmetric Universe. The formation of the 3-dimensional universe will be discussed in detail in a later section.
This new theory remains at a conceptual stage in many respects, and further work is proposed to justify its underlying assumptions. Earlier, it was suggested that the Universe is filled with an imaginary medium, viz. Aether. Here, energy symmetric space-time* quanta replace the Aether and justify wave-particle duality at the subatomic level. Preliminary justifications for this theory are presented by comparing it with Special Relativity, offering a more fundamental understanding of Special Relativity, Entropy, the expansion of the Universe, entanglement, and the arrow of time. It also aims to explain wave-particle duality and the uncertainty principle more realistically. The reasoning of the particle-wave duality in the Double slit experiment is established with this theory.
Space dimension and time dimension
The current theory extends the framework previously proposed by the authors [1,2], which posits that the energy source of the entire Universe originates from outside the Universe. In that earlier article, two external dimensions, “O-Reality” and “O-Imaginary,” were proposed. Here, these names are revised to “Space” and “Time*” dimensions.
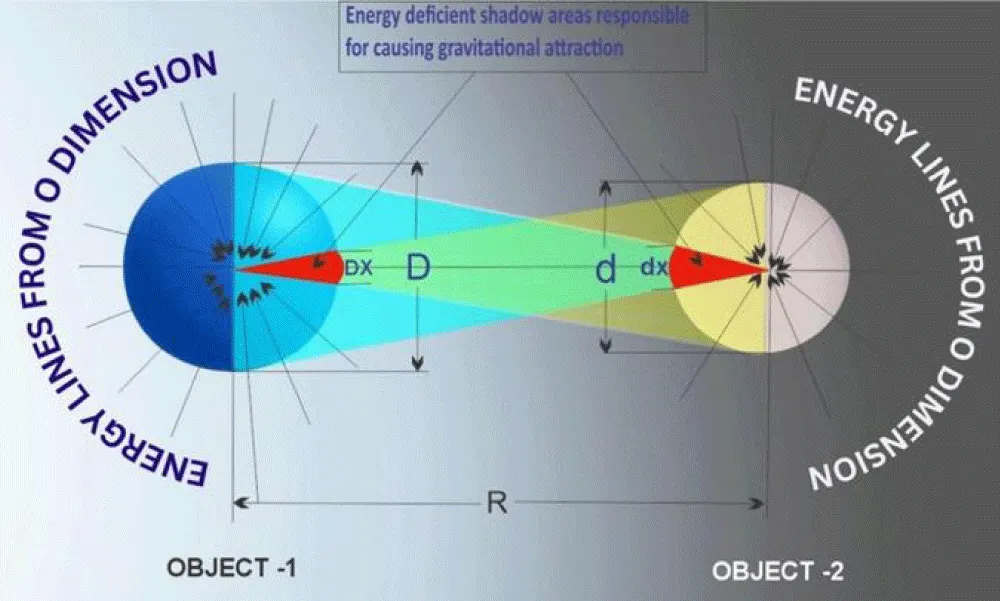
A brief overview of the earlier article’s concept is as follows: it introduced the idea of an external energy source, proposing that this source provides energy to the fundamental forces of every subatomic particle. This concept was supported by calculations of gravitational forces between the Sun and the planets of the solar system, as well as between the Earth and the Moon. These calculations were derived as a function of the “energy shadow” cast by these celestial bodies on each other. In this theory, the gravitational force arises from an energy deficiency caused by the mutual casting of these energy shadows. The gravitational force calculated using this theory matched Newtonian values (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Energy shadow picture. Energy shadow is the cause of a gravitational force.
An alternative view on gravity
Our theory proposes a novel explanation for gravity, conceptualising it not as a curvature of spacetime but as an “energy deficiency” caused by the presence of matter.
Every object, composed of Space-Time* quanta, acts as a barrier, shielding an external, continuous energy source. This shielding effect creates an energy deficiency in its “shadow.” Other objects moving into this region of lower energy density are propelled toward it, a phenomenon we observe as gravitational attraction.
- Deriving the force of gravity: We can model this by considering the energy deficiency (ΔE) caused by an object with mass M at a distance R. This energy deficiency is proportional to the object’s mass and inversely proportional to the area it projects onto the external energy flow.
Gravitational force calculation
The gravitational force was calculated using the equation:
GRAVITATIONAL FORCE = 2×7.978975×G×MCS1×MCS2/(Dx/2)^2 (1)
Where:
- MCS1 is the mass of the shadow cone of Object 1, which is starved for energy (Unit kg)
- MCS2 is the mass of the shadow cone of Object 2, which is starved for energy (Unit kg). It is assumed that MCS1 > MCS2.
- C = Velocity of light 3 × 108 m/s
- R = shortest distance between two objects
A new proposed equation for gravitational force, incorporating the Universal Gravitational Constant, is also presented:
GRAVITATIONAL FORCE = 2×7.978975×G×MCS1×MCS2/(Dx/2)^2 [2]
Here, G is the universal gravitational constant:
6.743×10−11 m3 kg−1 s−2.
Hans Hermann Otto [4], Further modified equation 2 to:
(4)
R Centre to Centre distance between the two objects, and r1 and r2 are the radii of the two objects.
The results of the calculation with the new formula were almost the same as equation (2).
A comparison of gravitational force calculations using this new proposed theory versus Newton’s formula is presented in Table 1.
| Table 1: A comparison of gravitational force calculations using this new proposed theory versus Newton’s formula | |||||||||||||
| C:Velocity of Light+ 3*10^8 M/S; G(Gravitational Constant)=6.743*10^-11 m3 kg-1 s-2 | |||||||||||||
| Star / Planet | Mass (kg) | Density (kg/m3) | Diameter (meters) | Distance from Sun/Earth | Diameter of bigger cone bottom (Dx) meters | Diameter of smaller cone bottom (dx) meters | Volume of sphere section of big cone M^3 | Volume of sphere section of small cone M^3 | Mass of bigger cone (M) Kg | Mass of smaller cone (m) kg | F = 2*7.978975*G*M*m/(Dx/2)^2 Newtons | F (By Newton's Formula) Newtons | F/F (newton Formula) |
| SUN | 1.989E+30 | 1410 | 1.39E+09 | 59146.48461 | 59146.48461 | 6.37112E+17 | 2.23341E+15 | 8.9833E+20 | 1.2127E+19 | 1.32645E+22 | 1.30638E+22 | 1.015362916 | |
| Mercury | 3.285E+23 | 5430 | 4879500 | 57419000000 | 59146.48461 | 59146.48461 | 6.37112E+17 | 2.23341E+15 | 8.9833E+20 | 1.2127E+19 | 1.32645E+22 | 1.30638E+22 | 1.015362916 |
| Venus | 4.868E+24 | 5243 | 12107000 | 1.08E+11 | 78022.88889 | 78022.88889 | 1.10867E+18 | 9.64281E+15 | 1.5632E+21 | 5.0557E+19 | 5.53099E+22 | 5.53822E+22 | 0.998694237 |
| Earth | 5.972E+24 | 5510 | 12742000 | 1.52E+11 | 58325.76126 | 58325.76126 | 6.19553E+17 | 5.67125E+15 | 8.7357E+20 | 3.1249E+19 | 4.31862E+22 | 3.54146E+22 | 0.965311632 |
| Mars | 6.417E+23 | 3933 | 6779000 | 2.18E+11 | 21649.00431 | 21649.00431 | 8.53559E+16 | 4.15682E+14 | 1.2035E+20 | 1.6349E+18 | 1.78856E+21 | 1.639E+21 | 1.091256371 |
| Jupiter | 1.898E+27 | 1326 | 139822000 | 7.43E+11 | 131005.4817 | 131005.4817 | 3.12562E+18 | 3.13959E+17 | 4.4071E+21 | 4.1631E+20 | 4.55445E+23 | 4.16494E+23 | 1.093520382 |
| Saturn | 5.683E+26 | 687 | 116460000 | 1.48E+12 | 54912.37721 | 54912.37721 | 5.49159E+17 | 4.59447E+16 | 7.7431E+20 | 3.1564E+19 | 3.45312E+22 | 3.66285E+22 | 0.936749448 |
| Uranus | 8.681E+25 | 1270 | 50724000 | 2.95E+12 | 11983.67413 | 11983.67413 | 2.61539E+16 | 9.53042E+14 | 3.6877E+19 | 1.2104E+18 | 1.32414E+21 | 1.39852E+21 | 0.946816822 |
| Neptune | 1.024E+26 | 1640 | 49244000 | 4.47E+12 | 7660.324527 | 7660.324527 | 1.06869E+16 | 3.78065E+14 | 1.5069E+19 | 6.2003E+17 | 6.78313E+20 | 6.68479E+20 | 1.014711452 |
| Pluto | 1.309E+22 | 1880 | 2376600 | 5.71E+12 | 289.6871454 | 289.6871454 | 1.52796E+13 | 2609353659 | 2.1544E+16 | 4.9056E+13 | 5.36544E+16 | 5.54741E+16 | 0.967197185 |
| Moon | 7.348E+22 | 3340 | 3474800 | 384400000 | 57590.923 | 57590.923 | 5.52925E+15 | 1.50795E+15 | 3.0466E+19 | 5.0365E+18 | 1.97099E+20 | 2.027E+20 | 0.972369844 |
Space-time quantum*
The space-time* quantum is hypothesised to form from the merger of a “time quantum” into a “space quantum.” This space-time* entity is thus a combination of two energies:
- Space energy: This is a form of potential energy that encapsulates and surrounds the internal kinetic energy.
- Kinetic energy of vibration: This is referred to as “Time* energy.”
Thus, a space-time* quantum is the energy combination of both space energy and Time* energy. Commonly, a quanta is defined as a tiny entity in size. Here, Space-Time quanta are tiny entities in terms of total energy content, rather than size. The size of space-time* quanta could vary from a kilometre to a Planck length.
Time
In this article, the term “Time” carries two distinct meanings:
- Time* (or T*): This refers to an inherent property of every object in the Universe, from fundamental particles like photons, electrons, and quarks, to macroscopic objects like planets and even the Universe itself. It is defined as the reciprocal of the object’s inherent frequency. Given that subatomic particles are known to consist of vibrating entities at specific frequencies, we define the Time* of such an entity as the reciprocal of its frequency. Larger objects, including planets, various materials, and living creatures, also possess an aggregate frequency derived from their constituent parts, and thus, an associated Time*.
- Time (or T): This is the conventional measure of events in our daily lives, expressed in units like seconds, minutes, hours, days, and years.
Space-time* quanta are not fixed in size. They represent the lowest-energy combination of space and time quanta. Later in the article, it will be demonstrated how the size of space-time* quanta varies with the expansion of the Universe. As the Universe expands, older quanta stretch more, leading to an increase in their potential energy (quanta size) and a decrease in their kinetic energy (quanta frequency).
The authors propose that time is more fundamental to nature than merely a dimension of the Universe, as Einstein envisioned. Every object in the Universe possesses a unique Time* value or a Time* to volume ratio (Time* density). Since fundamental Time* is the reciprocal of frequency, it implies that every object in the Universe has a unique frequency density.
Therefore, the concept of a “SPACE-TIME* quantum” is introduced. A space-time* quantum is composed of a “space quantum” and a “time* quantum”. It is described as a small, hollow fraction of space (the space quantum) that is inoculated with a vibrating frequency (the Time* quantum). Similar to energy, the quantum space-time* is a minor energy constituent of the Universe. Its size is not necessarily the smallest, like Planck’s value. Instead, its length is proportional to the oscillating Time*-frequency within it. It possesses an energy equal to hν (where h is Planck’s constant and ν is the frequency). All space-time* quanta of the fundamental universe are equal in total energy but can vary significantly in size, depending on their vibrational frequency and the potential energy of space.
The time value that we use in our day-to-day life is derived from the speed of light in a vacuum(c = 299,792,458 meters per second (m/s)) in our part of the Universe. This time is a function of the average asymmetry of our part of the Universe. Further in the article, the asymmetry and 3-D universe where we live are explained. The same base units are used in quantifying the intrinsic Time* of the objects.
Dimension
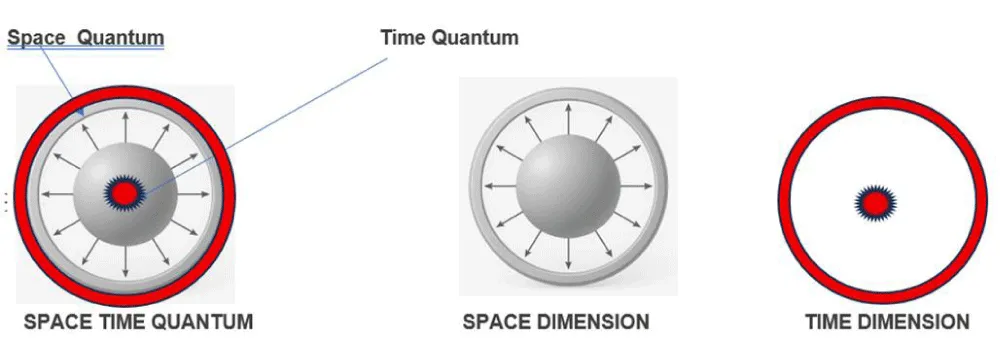
The fundamental building block of the Universe is a SPACE-TIME* quantum, defined as a superposition of space and time* quanta. The diameter of the space-time* quantum is proportional to the wavelength of the oscillating frequency inside it. The energy of a space-time* quantum is equal to hν, where h is Planck’s constant and ν is the frequency of oscillation of the time quantum (Figure 2).
Figure 2: The Fundamental building block of the universe is defined as a SPACE-TIME* quantum, which is a superposition of space and time* quanta.
The following equations are used as basic assumptions of the theory:
- Energy E of any particle = hν which is also proportional to ½ mv^2. So, it implies ν ∝ V^2. We are transitioning from classical physics to quantum physics in this assumption, considering E = hν and E = pc. This leads to the equations p = h/λ and V = νλ, as the boundary between classical matter and quantum matter becomes increasingly blurred.
C = νλ or V = νλ (3)
Where:
- c = speed of light in a vacuum (≈3×108 m/s)
- λ (lambda) = wavelength (meters, m)
- ν (nu) = frequency (hertz, Hz = cycles per second)
- V = velocity of particle or object, which is different from C but close to C.
- p represents momentum property
The diameter of a space-time* quantum could range from kilometres down to Planck’s size on the most minor scale. Higher frequencies correspond to smaller wavelengths. All Space-Time* quanta possess the same total energy value, but their potential and kinetic energy values can differ. Larger volume quanta have higher potential energy but lower kinetic energy.
Every space fraction within a space-time* quantum is part of the overall space quantum of the Universe (Space Dimension); similarly, every Time* fraction of a space-time* quantum is part of the overall Time* quantum of the Universe (Time Dimension). All space quanta originate from one original space quantum and are interconnected; similarly, all Time* quanta originate from one original Time* quantum. External energy input causes the fragmentation of space quanta into smaller space quanta and smaller Time* quanta. Space quanta represent a form of potential energy, and thus, Time* does not exist in the overall space quanta or the space fraction of space-time* quanta. Space quanta belong to the space dimension and, when separated from time quanta, are omnipresent in the universe as they are devoid of time*.
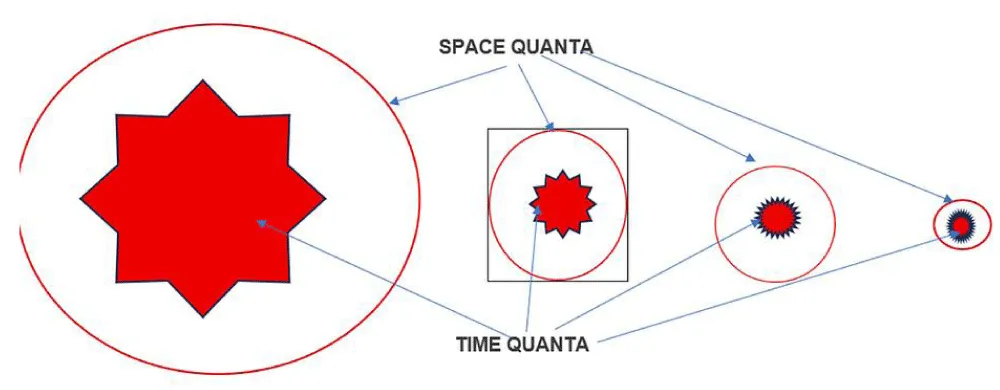
Space-time* quanta can have different frequencies (Time* values). Still, the total energy of all space-time* quanta (the kinetic energy of Time quanta plus the potential energy of space quanta) is identical, following Equation (3). Larger space quanta have higher potential energy and lower frequency, hence lower kinetic energy. Being similar in energy, all space-time* quanta ultimately converge to the same average “day-to-day time” value, which is the reciprocal of C, the speed of light for the basic foundational universe (Figure 3).
Figure 3: Space-time quanta (space shrinks as time shrinks, which is a result of an increase in frequency).
As frequency increases, Time* decreases. As Time* becomes smaller, the wavelength also becomes smaller, leading to the shrinking of the space quanta. This indicates that an increase in the vibration frequency of Time quanta results in a decrease in the Time* value and a reduction of wavelength.
Space quanta are part of the O-Imaginary dimension (now renamed as the “Space dimension”), and Time quanta belong to the O-Reality dimension (now renamed as the “Time dimension”). These O-Dimensions (Space and Time* dimensions) encircle every particle of the Universe individually, as well as larger objects cumulatively, and further encompass the entire Universe (Figure 4).
Figure 4: Dynamic space-time quantum [3]. (If animation is not visible, copy the links above and paste them into your browser.). https://www.youtube.com/post/UgkxT_al3ufAEg6SdJWDk6xyg5OJLdDHOwDa
This figure conceptually illustrates a Space-Time* quantum under the influence of two forces. These two forces act on each space-time* quantum and, consequently, on the entire Universe:
- The kinetic energy of the Time* fraction of the quantum.
- The potential energy of the space part of the quantum.
Beginning of the universe against big bang
The origin: The universe did not begin from an infinitely dense point. Instead, it was initiated by a single Space-Time* quantum, which was formed by the merging of space and Time* quanta. This initial quantum, containing a fraction of energy from both components, began to proliferate. The continuous addition of external energy led to the expansion of this quantum field.
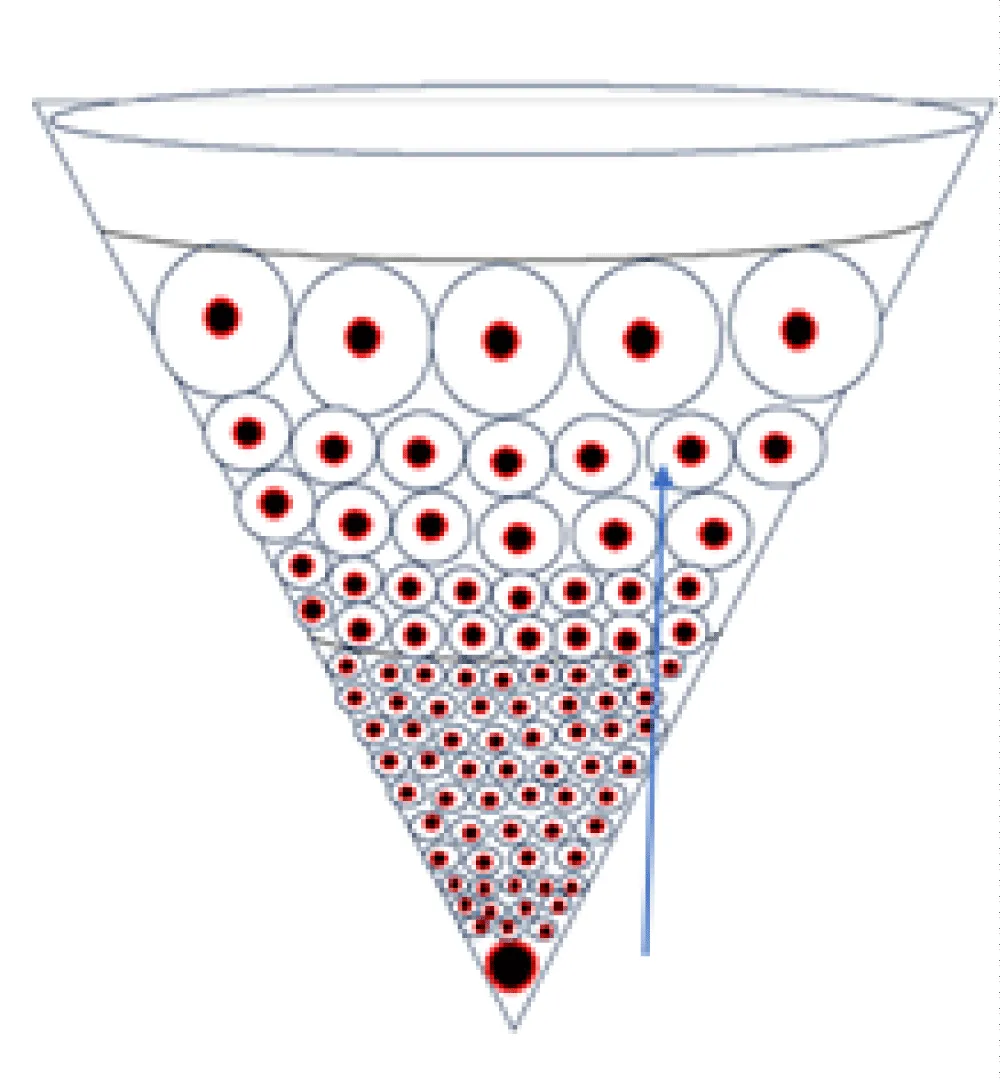
The theory presented here posits a beginning of the Universe that is almost opposite to the Big Bang theory. In this proposed theory, a Space quantum and a Time* quantum meet and merge to form a first space-time* quantum. The Space quantum, possessing potential energy having an origin in space dimension, stretches and pulls space along its circumference. In contrast, the Time quantum receives energy from an external source, creating vibration within the Space-Time* quantum. The energy imparted by these two sources accumulates within the space-time* quantum until it reaches its threshold limit. Upon reaching this threshold, a new Space-time quantum begins to form as both the space fraction and Time* fraction of the space-time* quantum split, giving rise to the creation of a new space-time* quantum. This process then continues (Figure 5).
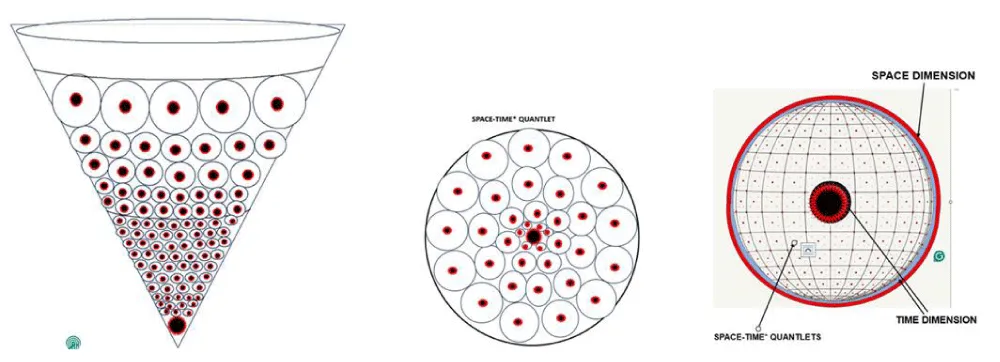
Figure 5: Formation of Space-Time*: Conical section of Space-Time* in the formation, and the second picture is of a bunch of Quanta, and we call it Quantlet. The fourth picture is the Universe filled up with Space-Time* Quantlets
The first quantum was characterised by higher Time* energy and lower Space energy. To counteract the force exerted by Time* energy, space pulled the quantum outward, thus expanding space. When the energy of a quantum reached its threshold value, further energy addition resulted in the creation of a new quantum. This process continues. As the Universe grew, the expansion force to counter the Time* force increased across the overall Universe, setting the Universe into an expansion mode. Older quanta grew in size due to this expansion force but experienced a decline in Time* force, while maintaining constant total energy. In the figure above, the second picture represents a fully grown bunch of Quanta (Quantlet). In this conceptual article, we assume that after a certain amount of growth of Space-Time quanta, leading to what we call a fully grown Quantlet, the formation of a new Quantlet begins.
Further in this article, the formation of the 3-D Universe will be explained. It has been proposed that the formation of the 3-D Universe began with the introduction of an asymmetric quantum into the Universe. During the growth of the Universe, its overall symmetry was preserved, and to maintain this property, the concept of multiple identical Quantlets is introduced.
Conservation of energy: The Law of conservation of energy is applicable, taking into consideration the Universe in combination of two dimensions, viz., space and time* dimensions. The universe, excluding the Space and Time dimensions, is undergoing continuous formation as well as expansion. Kinetic energy input from the Time* dimension gets converted to particle or Potential energy due to the expansion of space using energy input from the space dimension. Due to constant conversion of energy to mass or particles, measurable energy of the Universe remains constant, excluding Space Time* dimensions.
Why an expanding universe?
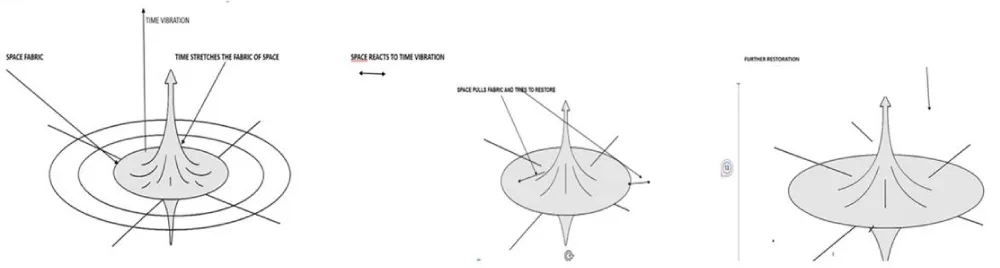
Two forces are acting on the Universe. A vertical force represents the force exerted by time, and a horizontal force represents the force exerted by space. The vertical force creates a new universe, while the horizontal force in the spatial dimension pulls back the universe stretched by the time dimension. The total addition of energy results in a larger, expanding universe. The space dimension absorbs the force exerted by the time dimension. The net result is the addition of two energies, which results in the continuous formation and expansion of the Universe. Two dimensions act in opposite ways, and hence, the creation process of the Universe is not apparent (Figure 6).
Figure 6: Time pulse creates a low entropy peak in space, and tension in space results in the expansion of the space, increasing entropy.”
Two forces are acting on Space-Time*. Time* imparts kinetic energy, and space imparts potential energy to restore space. The energy for the Time* force is imparted by the O-Reality Dimension (nomenclature used in previous articles 1, 2) or the Time dimension. The restoring force on the space fabric is imparted by the O-Imaginary dimension (nomenclature used in previous articles 1, 2) or the space dimension. The authors previously used the nomenclatures O-Reality and O-Imaginary dimensions for the Time* and space dimensions.
The Time* dimension and space dimensions encircle every Space-Time* quantum, and subsequently, the aggregated space-time* quanta, and further encompass the entire Universe. Every space part of a space-time* quantum is connected to or is a part of the whole Space dimension, and similarly, every Time* part of a space-time* quantum is connected to or is a part of the entire Time* dimension. The space quanta fraction is free from time, and its movement in a dynamic universe is instantaneous. This property helps explainthe constant speed of light and wave-particle duality, as discussed later in this article.
Entropy and the arrow of time
The Time dimension creates a new Universe, which establishes a lower entropy region within the whole space-time*. Concurrently, space pulls the space-time fabric, resulting in its expansion and an increase in entropy, which provides a direction to the arrow of time.
Why is the speed of light constant in all frames?
Immediately after its formation, the Time* part of a Photon space-time* quantum separates from its Space quantum. The Time fraction, or vibration, travels through an ocean of space-time* quanta at speed “C”, while the space fraction, being timeless, is omnipresent throughout the Universe and instantaneously meets its Time* fraction counterpart at the point where the photon is observed. Due to the merger of space and Time* at the observation point, the photon becomes a particle and becomes visible. Therefore, we are aware of the starting position of the photon and the final position where it is observed. In the interim, only the wave is travelling, and it meets the space fraction at the point of observation. Thus, the velocity of light is independent of any observation frame, as its travel path is invisible. From any frame, only the starting and final points are visible, which is why the observed time remains constant from every frame.
Speed of light and current status of the universe
The speed of light “C” that we observe is a consequence of the current Time value of our 3-D Universe, where we reside. The average Time* density value, in turn, depends on the average asymmetry of the current Universe. The speed of light is c = 299,792,458 meters per second (m/s), and remains constant as per equation (1). Time dilation is dependent upon the Time* density value. Time (Hours, minutes, and seconds) is slower in the part of the Universe where Time* density is low. This Time value or speed of light is due to the current asymmetry of our universe’s neighbourhood. The speed of light and the current time of day-to-day life could vary in different parts of the Universe. This statement is in little departure from Einstein and Maxwell’s theories. When we restrict to a smaller part of the Universe and consider the average asymmetry of that part, the Time* value is decided for that specific portion, and Maxwell and Einstein’s principles are well applicable for that part of the Universe.
Formation of A3-D universe
Three factors influenced the formation of a 3-D universe inside the Space-Time equal energy space-time* quanta ocean
- Introduction of asymmetry
- Superposition of Information onto Time* quanta
- Superposition of consciousness onto Time* quanta
Information, consciousness, and the 3-D universe
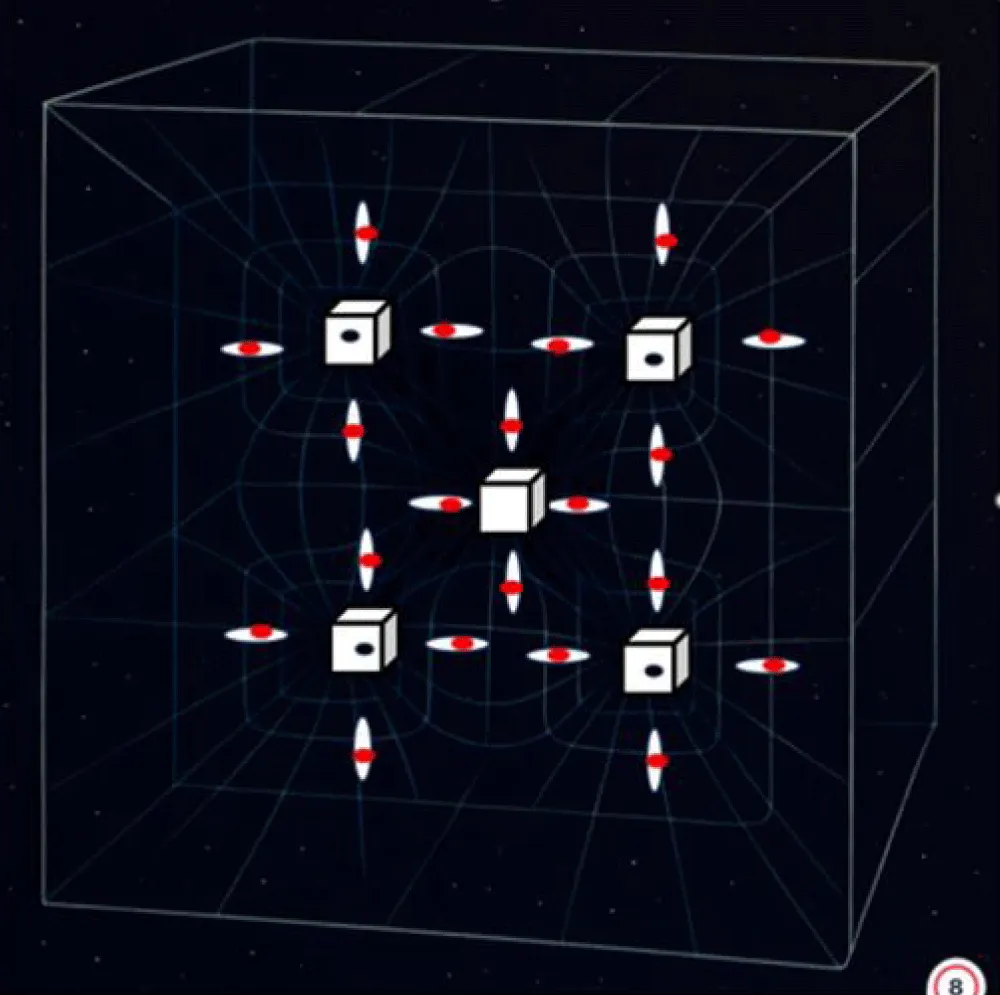
This theory proposes that an initial Universe comprised only of energy-symmetric space-time* quanta. To create a 3-D Universe, an asymmetry must be introduced into this initially symmetric Universe (Figure 7).
Figure 7: Information, consciousness, and the 3-D universe”. Asymmetry entry into the quantlet of space-time*.
This asymmetry is proposed to be generated by a “new energy quantum” (the Time* quantum) that is distinct from the Time* quantum that is already a part of the space-time* quantum. This new Time* quantum, when introduced into the symmetric ocean of space-time* quanta, disrupts their uniform vibration and distribution, thereby generating asymmetry. This asymmetry leads to a random movement of the space-time* quanta.
Furthermore, it is proposed that information is superimposed onto this new Time* quantum. This information acts as a guiding principle, much like DNA in a living cell, directing and disciplining the otherwise random movement of the space-time* quanta. This directed movement is crucial for the formation of the ordered, three-dimensional structure of our Universe.
Consciousness is defined in this theory as the ability of an entity to sense its surroundings and interact with them. It is posited that consciousness generates an electrical charge on objects, enabling them to interact with other particles in their vicinity. The theory also suggests that properties such as anger, greed, desire, arrogance, and love in living beings arise from this consciousness parameter (Figure 8).
Figure 8: Introduction of asymmetry in the equal energy ocean of space-time* quanta led to the formation of a 3-D universe [5].
The above figures illustrate the process of formation of a 3-D Universe. Figure 8B(ii) shows vibration due to the time dimension for the formation of the up quark; Figure 8B(i) shows vibration due to the Time dimension for the formation of the down quark; Figure 8B(iii) shows space confines the up and down quark, resulting in the formation of a particle.
Figure 8B: Time vibration of Down Quark (i), Up Quark (ii) and, which gets confined (iii) by the space dimension. (i) Down Quark: https://medium.com/r/?url=https%3A%2F%2Fenergywavetheory.com%2Fwp-content%2Fuploads%2F2014%2F11%2Felectron_statique.gif (ii) Up Quark: https://energywavetheory.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/11/Inwaves.gif (iii) Up and Down Quark Bound by space: https://energywavetheory.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/11/Inwaves1.gif (If animation is not visible, copy the links above and paste them into your browser.)
A proton is made of three quarks:
- 2 up quarks (u)
- 1 down quark (d)
Why does Proton have a Positive Charge?
As per the standard theory explanation is as follows;
Each quark has a fractional electric charge:
- Up quark: +2/3
- Down quark: -1/3
Total charge of a proton: A Proton has 2 up quarks and 1 down quark, whereas a Neutron has 1 up quark and 2 down quarks
Below is the positive charge calculation of a proton:
2 × [+(2/3 )] + (-[1/3]) = +1
And below is the calculation of the neutral charge on Neutron:
+(2/3 ) + 2 × [-(1/3])] = 0
So, the sum of the quarks’ charges gives the proton its +1 electric charge and the neutron its 0 charge.
According to current theory, the allocation of +2/3 charge to the up quark and -1/3 to the down quark is due to the information and consciousness transmitted by asymmetric space-time quanta, which entered into the basic symmetric foundational universe. The same asymmetric quanta are responsible for the creation of a negative charge on an electron. The time* dimension imparts not just the vibrational force to quarks but also a force to hold them together, which is called the Strong Force in the standard theory. This force confines nucleons in space, forming a particle called the Nucleus. Without the strong force from the time* dimension, the neutron could not have held quarks together. Similarly, the interaction between the Time force and the spatial force generates a field that governs electron rotation. The Standard Model does not provide an intrinsic explanation or picture for the localisation of electrons in a particular region; it instead relies on the Heisenberg uncertainty principle and states the impossibility of achieving high-momentum electrons. This current theory provides a rationale for electron field formation based on fundamental principles. Proper visualisation of particle behaviour in infinite or finite wells is possible using the current theory.
In quantum field theory, quantum fields are the fundamental properties of the Universe, but they do not explain how these fields arose; by contrast, current theories provide insight into how they formed.
Big bang expansion of the universe explained in the perspective of current theory
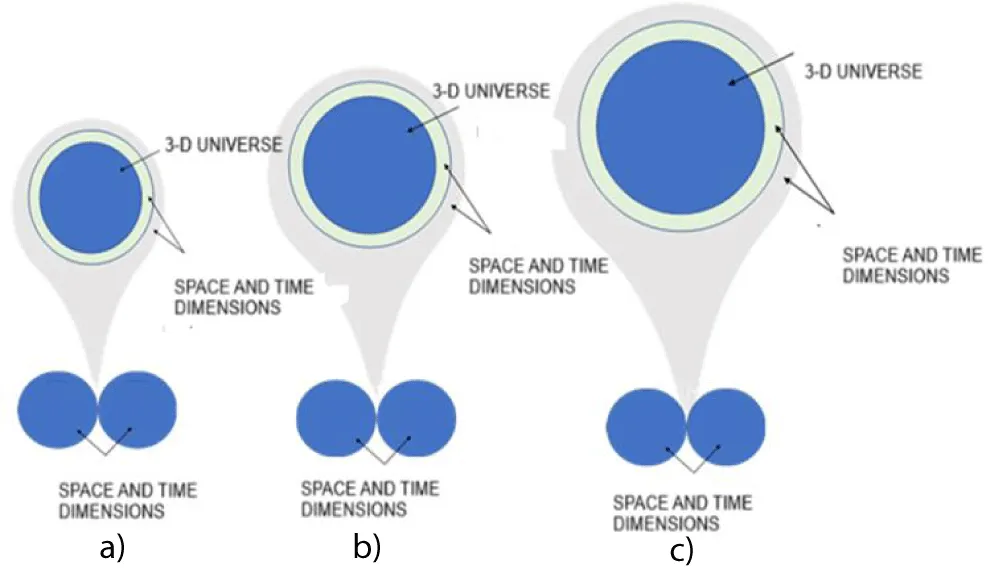
Expanding 3-D universe (Figure 9)
Figure 9: a-c)Time density value decreases as the universe expands.
The universe is shown at its three stages of expansion conceptually
The velocity of light C is the same in all three stages when observed in their frames.
The time* density of the universe differs in these stages. Hence, the relative velocity of light increases with expansion when observed from the expanded frame of the universe.
Hence, the speed of light of stage (a) concerning other stages is higher when observed from other stages; similarly, for every stage, the speed of light is observed to be higher compared to the expanded state when observed from the expanded state.
The wavelength of light of every stage is lower than that of the expanded stage when observed from the expanded stage. A redshift is the result of a change in the relative period of the Universe as it expands. When an object from the distant past is observed from the expanded state of the universe, the observed value has a higher wavelength of light and a lower frequency. This is the cause of the observed redshift.
As the asymmetry and volume of the Universe increased, the value of time density decreased. The current value 1/(3*10^8) seconds/meter (the reciprocal of the velocity of light) is the representative current state of asymmetry of the Universe. Thus, the speed of light is nothing but the degree of asymmetry of the Universe, and it is a fundamental value of the current state of the Universe. The time* density of the 3-D universe has been decreasing over very long periods as the Universe expands. Additionally, the velocity of light regularly increases with the expansion of the universe when observed from the expanded stage of the universe. A decrease in time* density value results in an increase in entropy value. Since our Universe is growing continuously, the time density is decreasing. This is the reason for time appearing to be Unidirectional. Thus, time and entropy are functions of the degree of asymmetry. The increasing entropy property is due to the continuous expansion of the Universe. In a 3-D universe, a photon appears to travel from one point to another, whereas when viewed from the space dimension, it is already at those two points in the beginning itself. The phenomenon of light travelling is a property of the 3-D universe due to the presence of space and time, and it is different when observed from the spatial dimensions. A photon in a 3-D universe is a projection of a photon in the spatial dimension. Movement of a photon in a 3-D universe is governed by the dynamics of the energy gap between space-time* energy sources, and the degree of asymmetry creation. These dynamics of vibration from an external energy source and the degree of asymmetry lay the foundation of current laws of Physics.
The Big Bang theory states a sudden expansion for the creation of the Universe. From the perspective of current theory, the Big Bang is an illusion due to the declining Time* density of the Universe.
Also, current theory proposes the beginning of the universe from a single quantum and its further expansion by the addition of energies from space and time dimensions; it matches the observation of Isotropy, which supports the Big Bang theory.
Special relativity from the perspective of space-time quanta
This Space-Time* quanta theory merges Special Relativity with quantum mechanics and offers a better visualisation of Special Relativity. Special Relativity proposed time dilation and space contraction at high velocities of objects or particles. This phenomenon can be better visualised and understood at a fundamental level through the current theory. Below is an explanation of Special Relativity from the perspective of the current theory.
As the Universe expands, outer space-time* quanta are stretched more than the inner, younger space-time* quanta. Consequently, space quanta are larger in volume compared to younger quanta. As particle velocity increases, its space quantum gets stretched, and its Time * density value decreases, causing it to shift to the outer area of low Time * density within space-time * (Figure 10).
Figure 10: As the object is accelerated, its space-time quanta move such that the space fraction of the quanta has enough potential energy to withstand the energy gain of the quanta. So space expands. Wavelength increases.
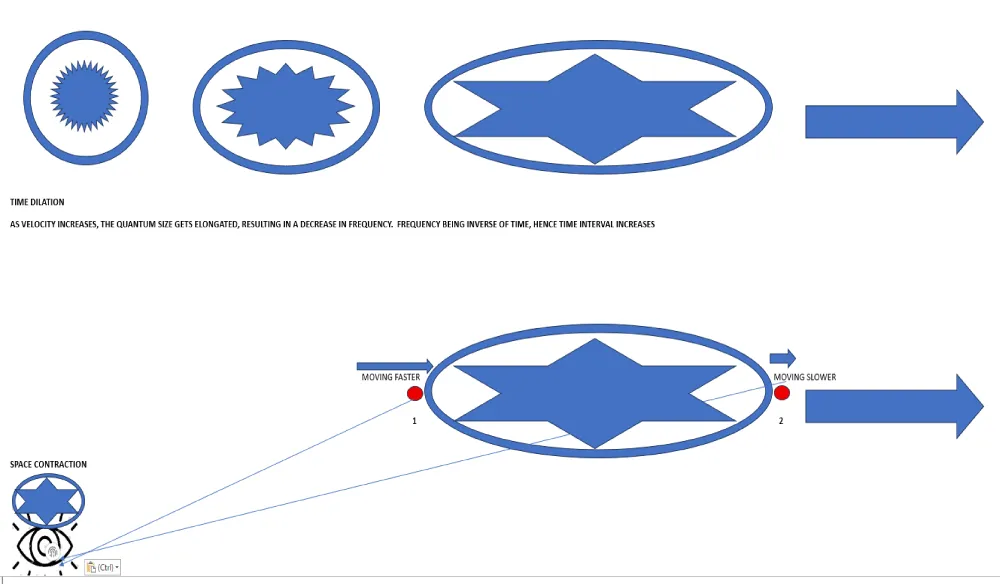
Time dilation and length contraction (Figure 11)
Figure 11: Time Dilation and Length Contraction.
Time dilation:
In Special relativity, Einstein applied the Lorentz factor to space-time geometry to arrive at Time dilation and Length contraction expressions. The Lorentz factor was derived using the property of the constancy of light velocity.
The time dilation property of Special Relativity is better visualised and supported by the current Space-Time* quantum theory. As wavelength increases, frequency decreases according to the equation (ref: Figure 3):
C = νλ or ν∝ (1/λ) (4)
According to current theory, ν represents Time* part of space-time* quanta, whereas λ is proportional to the size of space and represents space fraction of space-time* quanta. As velocity increases, λ increases and λ ∝ 1/V.
Kinetic energy, as per quantum physics, is hν2, and classical physics is ½(mV2). At subliminal velocities, the boundary between classical physics and quantum physics is blurred. Hence
- c = speed of light in a vacuum (≈3×10^8 m/s)
- V = velocity
- λ (lambda) = wavelength (meters, m)
- ν (nu) = frequency (hertz, Hz = cycles per second)
The intrinsic time of the quantum is the reciprocal of its frequency:
T* intrinsic=1/ν
Let:
- T1: Intrinsic time interval of quanta for a fixed distance (Observer Frame)
T1* is the dilated time as the object's velocity reaches subluminal velocity
- T2: Intrinsic time interval of quanta for a fixed distance (observer frame) at Velocity “C.”
- ν1 : Frequency of the object at Velocity V1
- ν2: Frequency of the object at Velocity C
- ΔT = T1-T2
- T1∝ λ1∝ 1/ν1∝ 1/V1²
- T2∝ λ2 ∝ 1/ν2∝ 1/V2²
- V= velocity
- C = Light velocity
- Δ(T)/T1=(T1−T2)/T1
Δ(T²)/T1²=(T1²−T2²)/T1²
Δ(T²)/T1²=(λ1²−λ2²)/λ1²
= [(1/V1²) –(1/C²)] /(1/V1²) …… V2=C
=1-(V1² / C²)
Δ(T²)/T1²= 1-(V1² / C² )
Δ(T²)= (1-(V1² / C² ))* T1²
T1²=Δ(T²)/( 1-(V1² / C² ))
T1=√[Δ(T²)/( 1-(V1² / C² ))]
T1=√Δ(T²)/√( 1-(V1² / C²))
T1 = √T²/ √( 1- (V1² / C² ))
T^2=T1²−T2²
T2 is the Time observation at a velocity equal to C from the observer’s frame, which is equal to zero.
T1* = T1 / √( 1- (V1² / C^2 ))
T1* is the dilated time at subluminal velocity
1/√[1−(V12/C2)] is the Lorentz factor γ
T1* = T1γ
Hence, observed Time length increases as the object reaches velocity C. It is the Time dilation as per Special Relativity
Length contraction
Below is the comparison for Length Contraction with Special Relativity and Space-Time* quantum theory.
Let:
- Initial diameter of quanta before acceleration = L1
- Diameter of quanta after acceleration = L2
Length contraction = (L2−L1) = ΔL
ΔL/L1 = (L2−L1)/L1
Let:
- λ1 = wavelength of the moving object at velocity V1
- λ2 = wavelength at Velocity C
Δ(L)²/L1² = (L2²−L1²)/L1²
Δ(L)²/L1² = (λ2²−λ1²)/λ1²
The wavelength of quanta
Λ = 1/ν.
So,
Δ(L)²/L1² = (λ2²/λ1²)-1
Δ(L)²/L1² = [(1/ν2)²/(1/ν1)²]-1
Δ(L)²/L1² = [(1/V2)²/(1/V1)²]-1
LENGTH CONTRACTION is to be compared at velocity V approaching velocity C Hence: V2 = C
Δ(L)²/L1² = (V1²/C²)-1
Δ(L)² = [(V1²/C²)-1] *L1²
Δ(L)² = L2²-L1²
L2 is the length observed at a velocity of C, which is equal to zero.
Δ(L)² = -L1²
-L1*² = [(V1²/C²)-1] *L1²
L1* is the contracted length at the subluminal velocity of the object
L1*² = (1-V1²/C²) *L1²
L1* = √(1-V1²/C²) *L1
The factor
1/√[1−(V2²/C²) is the Lorentz factor γ. When speed reached Light speed, V2 = C, so the Lorentz factor becomes 1/√[1−(V1²/C²) Therefore:
L1* = L1/γ
Thus, the current theory satisfies the Special relativity condition of length contraction.
Thus current theory gives an explanation about Time dilation and space contractions based on fundamental properties instead of using geometric or mathematical constructs.
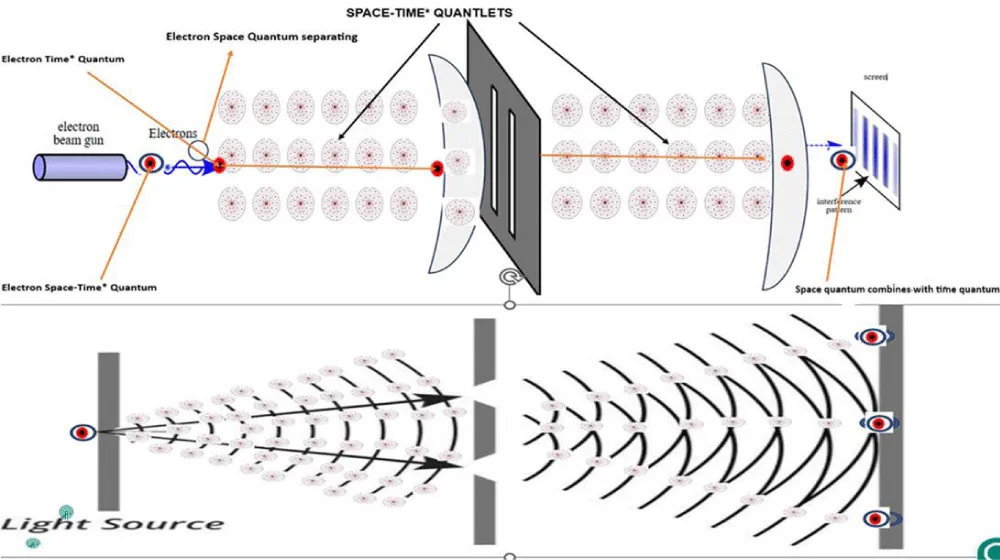
Double slit experiment (Figure 12)
The double-slit experiment has been a long-standing mystery for physicists. This theory offers a rational and visual explanation for the experiment and for wave-particle duality.
Figure 12: Double slit Experiment: Space quantum fraction of Space-Time* Quantum gets separated from time* fraction. Time* quantum travels like a wave through the Space-Time* Quantlets. Waves interfere with each other, and at the point of detection on the screen, the Time* quanta join the space quanta, becoming a particle, and an interference pattern appears on the screen.
When a photon or electron passes through a double slit, if both slits are open, the electron/photon exhibits wavelike behaviour.
As previously discussed, a space-time* quantum is composed of two parts: a space quantum and a Time* quantum. A photon or electron is a space-time* quantum. The Time* quantum, which possesses kinetic energy, separates from the space quantum during its travel. The Time* quantum, a vibrating entity, travels as a wave. The space quantum, which has potential energy and is timeless, is omnipresent throughout the Universe. This space quantum is connected to the time quantum only during observation, at which point the photon or electron becomes visible as a particle.
When an electron is released from a gun, it is in a particle state. As it travels, its Time* quantum detaches from the space quantum. The Time* quantum travels as a wave, while the space quantum, being timeless, instantaneously fills the space between the gun and the screen, remaining in a superposition state. It is the Time* quantum (the wave) that travels through the double slits. The Time* quantum is a wave, and when it encounters the double slits, it passes through both, creating an interference pattern on the screen. Space quantum joins time quantum and becomes a particle when the time wave hits the detector.
When the Time* quantum (wave) hits the screen, it immediately interacts with the omnipresent space quantum, and the resulting composite is observed as a particle. Due to the interference pattern formed by the wave travelling through both slits, multiple points of the interference pattern are observed on the screen.
Now, consider the case when only one slit is open. The Time* quantum, being a wave, travels through that single slit. Because there is no other slit for interference, it forms a single point on the screen. Again, when it hits the screen, it interacts with the omnipresent quantum field and is observed as a particle at a single location. Thus, the electron behaves like a particle when detected on the screen, but does not show an interference pattern.
Now, let’s consider the scenario where a detector is placed to observe which slit the electron passes through. When a detector is introduced, it implies that the Time* quantum (the wave) is made to interact with the omnipresent space quantum at the detector's location, thereby transforming it into a particle. Thus, the wave function collapses, and the electron behaves like a particle, leaving a single mark on the screen.
Quantum entanglement
Space quantum: Time split entangled quanta (Figure 13).
Figure 13: Entangled particles inside the common space quantum.
Quantum entanglement suggests that when two particles are entangled, measuring the spin of one instantaneously influences the spin of the other, regardless of the distance between them. This phenomenon, which Einstein famously called “spooky action at a distance,” can also be explained by the space-time* quantum theory.
In this theory, the Space quantum is timeless and omnipresent throughout the Universe, instantaneously connected from one end to the other. When two particles are entangled, their space quanta are interconnected or unified as a single space quantum. Consequently, when the Time* quantum of one particle is measured, it immediately connects with its Space quantum. Since this Space quantum is instantaneously connected to the Space quantum of the other entangled particle, the Time* quantum of the second particle also instantly connects with its respective Space quantum. This leads to the instantaneous manifestation of the entangled particle’s property upon measurement of the first. Space quantum has a variable size in a 3-D universe. So entangled particles can have the same space quantum of a very long length when viewed from 3-D space. When observed in the space dimension, there is no separation observed, like the observation from 3-D space.
Dark matter and dark energy
Energy calculations of the Universe have revealed that actual matter contributes to only 5% of the total energy content of the Universe, and the remaining 95% is due to Dark matter (27%) and Dark energy (68%).
- Stars in galaxies rotate at speeds that should decrease with distance from the centre (according to Newtonian gravity and visible mass).
- However, observations show the rotation speeds remain constant or even increase.
- This implies extra unseen mass — attributed to dark matter.
- The visible mass in galaxy clusters doesn’t account for the gravitational binding required to hold the cluster together
Dark energy:
- Type Ia supernovae are standard candles (objects of known luminosity).
- In the late 1990s, observations showed that distant supernovae were dimmer than expected, indicating the universe’s expansion is accelerating.
- This led to the concept of dark energy, driving that acceleration.
According to current theory, the time density of the Universe has been decreasing. Observed expansion rates or distances between objects from our frame are much higher than the actual values. There is a need to apply corrections to the calculation of Dark Matter and Dark energy using this factor. As explained earlier, the Big Bang is an optical illusion arising from the time-dilation effect associated with the decreasing density of the expanding Universe. This theory posits an external energy responsible for the existence of the Universe. The contribution of this energy should be evaluated in the energy Tally of Dark energy.
Superposition
The current theory offers a practical visualisation of superposition (Figure 7). A space-time* quantum is composed of both a space quantum and a Time* quantum. The space quantum is timeless, whereas the Time* quantum, a vibrating entity, is in constant motion. A space-time* quantum is said to be in a superposition of states as long as its Time* quantum has not been “observed” (i.e., forced to connect with its space quantum). Once the Time* quantum is “observed,” it connects with its space quantum, and the space-time* quantum then exists in a single, defined state, eliminating the superposition.
The quantum world: Observed and unobserved
As proposed in this article, the “unobserved” quantum world is the realm where the Time* quantum is in its natural state of vibration, separate from its space quantum during its free travel. It is the “observed” quantum world when the Time* quantum connects with its space quantum, making the space-time* quantum visibsle as a particle (Figure 11).
Gravity and its influence on space-time* quanta (Figure 1)
According to this new theory, the gravitational force that keeps objects in orbit, like planets around the Sun, is not an inherent property of space-time curvature, but rather a consequence of energy deficiency created by the shadow that objects cast upon each other, preventing the flow of energy from the O-reality (Time) and O-Imaginary (Space) dimensions. The effect of gravitational force is similar to the expansion force exerted by Time* (kinetic energy) and the restoring force exerted by space (potential energy). When two celestial bodies exist, they affect each other’s Space-Time* quanta. They form a combined space-time* quantum. This combined quantum state has less total energy than the sum of the individual objects' energies. This deficiency manifests as the gravitational attraction between the two objects.
Black holes
In this theory, the space surrounding a Black Hole (the Schwarzschild radius) experiences a significant increase in its space potential energy and a corresponding decrease in its Time* kinetic energy. At the event horizon of a black hole, the Time* kinetic energy of a space-time* quantum effectively becomes zero, while its space potential energy reaches its maximum. This leads to an increase in the size of the space-time* quanta in the vicinity of the black hole. When the Time* kinetic energy becomes zero, time itself ceases to exist for any object that crosses the event horizon. This explains why nothing, not even light, can escape a black hole once it has crossed this boundary. Little Bold and conceptual statement about black hole: At the event horizon, Kinetic energy (Time*) is squeezed out from the space quantum and only appears as information on the surface of the event horizon, and space fraction goes inside the event horizon, causing weight gain (potential energy increase) of the black hole. No Time* (kinetic energy or frequency) is emanating out from the black hole; hence, we do not see anything beyond the event horizon.
Wave functions
The authors think of defining a new wave function. A significant amount of work is required to arrive at the proper wave function. They believe that introducing Hilbert space in quantum physics is unnecessary, and that the concepts should be straightforward, similar to those in regular physics. Work will be done to check the justification of this feeling.
Quantum gravity
Reconciling gravity with quantum mechanics [6,7] remains a significant challenge in physics. This theory of space-time* quanta provides a potential framework for unifying these two pillars of modern physics. It posits that gravity arises from the energy deficiency in the fabric of space-time* quanta, caused by the mutual shadowing effects of objects on the external Time and Space dimensions. This offers a different perspective from the conventional view of gravity as a curvature of space-time.
GRAVITATIONAL FORCE =16×G×MCS1×MCS2* R²/(Dx*dx/4)² [1,2,4] will be applicable for quantum gravity as well as for Black holes. The authors propose to apply this equation to the unification of forces across all three domains of the Universe. Forthcoming research will be concentrated on this unification.
The proposed theory of Space-Time* quanta offers a novel and unified perspective on fundamental physics, providing a conceptual framework that aligns the key principles of quantum mechanics and relativity. The core idea of a Space-Time* quantum, a localised wave packet with an intrinsic Time* property, provides a physical basis for understanding phenomena that have long been difficult to reconcile.
By redefining the nature of time and space, this theory provides a new lens through which to view gravity, the expansion of the universe, and the very essence of matter. While this paper establishes a strong conceptual foundation, a more rigorous mathematical framework is required to test and validate its predictions. This theory provides a new and fertile ground for future research, offering a path toward a more intuitive and unified understanding of the universe.
- Bhandari PN, Bhandari NM. Fundamental forces are not fundamental as our 3-D universe is driven by an external energy source. Int J Phys Res Appl. 2023;6:167–179. Available from: https://doi.org/10.29328/journal.ijpra.1001068
- Bhandari PN, Bhandari NM. External energy sources and their influence on fundamental forces in our 3-D universe. Int J Sci Res (IJSR). 2023;12(8):371–383. Available from: https://www.ijsr.net/getabstract.php?paperid=SR23801092721
- Ethan SiegelEthan Siegel in Starts with a Bang! ∙ July 18, 2025 ∙ 12 min read Member-only content ∙ View on Medium.
- Otto HH. Reciprocity Relation between Alternative Gravity Formulas. Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics. 2024;12(4). Available from: https://www.scirp.org/journal/paperinformation?paperid=132923
- LaFreniere G. Matter is made of waves [Internet]. Blog. Available from: http://www.glafreniere.com
- Wilson KG. Confinement of quarks. Phys Rev D. 1974;10(8):2445–2459. Available from: https://journals.aps.org/prd/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevD.10.2445
- Schwarzschild K. On the gravitational field of a mass point according to Einstein’s theory. Sitzungsber Preuss Akad Wiss Berlin (Math Phys). 1916:189–196. Available from: https://arxiv.org/abs/physics/9905030